Workflows Examples
Almost daily since the release of Workflows 2.0, we continue to be amazed by the incredible workflows created by the Supercode community. However, our Workflows documentation looks extensive and the number of features can be a bit intimidating for new users, making it unclear where to start and how to avoid getting stuck.
We decided that the best help is to simply show examples of real Workflows that can be downloaded with one click and used in your project. Then - study how they work and start creating your own solutions for your specific tasks.
We've highlighted 5 examples:
- (Very simple) Send Telegram message at the end of work
- (Simple) Mandatory test execution
- (Simple) Ralph Wiggum aka "Ralph is a Bash loop" - iterative task solving
- (Medium) Multi-step refactoring
- (Advanced) Automatic Trello task processing - takes from Todo, executes, moves to Done
Send Telegram message at the end of work Very simple
You can download a ready-made workflow and use it in your project.
Simply extract the archive to the .supercode/workflows/ directory:
This example shows how to create a simple workflow for sending Telegram notifications after the agent completes its work. Perfect for long-running tasks when you want to receive a notification about their completion.
What does this workflow do?
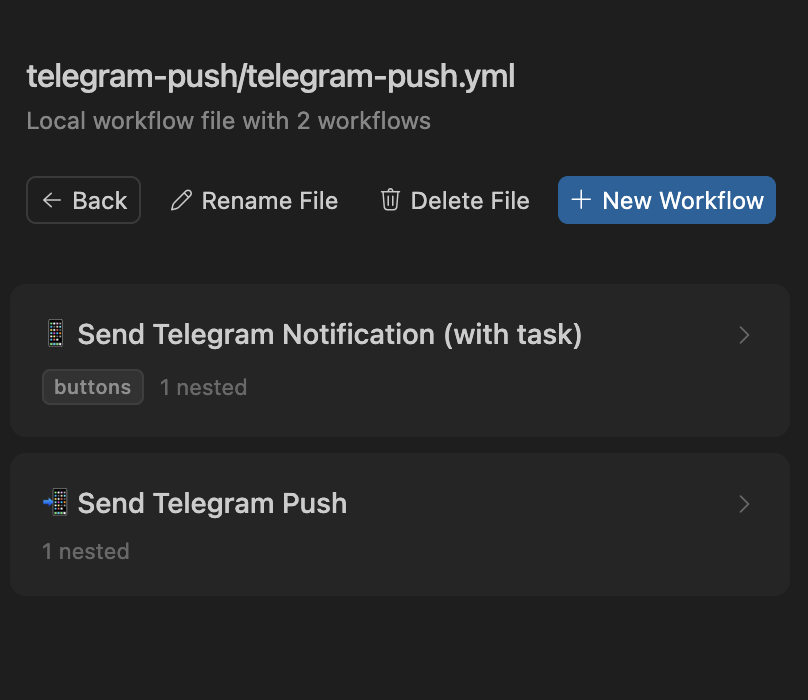
In this example, we create two workflows:
1. Send Telegram Notification (with task) - main workflow with a button in the UI. When you click it:
- Executes your current prompt
- Sends a notification to Telegram
- Clears the prompt
2. Send Telegram Push - auxiliary workflow without a button, designed to be used as the last step in other workflows. Takes a message from $prompt, sends it, and clears the prompt.
Setup
1. Create a Telegram bot:
- Open Telegram and find @BotFather
- Send the command
/newbot - Follow the instructions to create a bot
- Copy the bot token (looks like
123456789:ABCdefGHIjklMNOpqrsTUVwxyz)
2. Get Chat ID:
- Start a chat with your bot
- Send any message to the bot
- Open in browser:
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YOUR_BOT_TOKEN>/getUpdates - Find in the response
"chat":{"id":- this is your Chat ID
3. Configure environment variables:
Add the following variables to the .env file in the root of your project:
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN="123456789:ABCdefGHIjklMNOpqrsTUVwxyz" TELEGRAM_CHAT_ID="123456789"
If you don't have a .env file yet, create it:
touch .env echo 'TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN="YOUR_BOT_TOKEN_HERE"' >> .env echo 'TELEGRAM_CHAT_ID="YOUR_CHAT_ID_HERE"' >> .env
Important: Make sure .env is added to .gitignore to avoid committing credentials:
echo ".env" >> .gitignore
Usage
Option 1: Main workflow with button
Simply enter a task in the prompt and click the "Send Telegram Notification (with task)" button:
- Enter: "Refactor authentication module and add tests"
- Click the workflow button
- The agent will complete the task
- You'll receive a Telegram notification upon completion
Option 2: Use in other workflows
Add a reference to the workflow at the end of your own workflow:
Your Workflow:
icon: 🚀
menu: buttons
actions:
- name: Do Something
prompt: 'Analyze codebase'
instantRun: true
- name: Prepare notification
prompt: '✅ Analysis complete! Found 3 possible improvements.'
- 'Send Telegram Push' # Reference by nameFile structure
The workflow contains the following files:
telegram-push.yml- main file with two workflowsscripts/send-telegram.sh- bash script for sending messages.env.example- example environment variablesREADME.md- detailed documentation
Configuration is stored in the .env file in the project root (not in the workflow directory).
Mandatory test execution Simple
You can download a ready-made workflow and use it in your project.
Simply extract the archive to the .supercode/workflows/ directory:
This workflow ensures that tests will pass successfully. If tests fail, it automatically fixes errors and runs them again in a loop until all tests pass.
What does this workflow do?
Tests Must Pass is a workflow with a button in the UI that implements guaranteed test execution and fixing through smart state management:
- Runs tests - executes
npm testand captures output with exit code - Clears on success - if exit code is 0 (tests passed), clears the prompt
- Fixes and loops - if prompt is not empty (tests failed), fixes issues and returns to step 1
Loop mechanics
The workflow uses prompt state to manage the loop:
- Tests passed: Exit code = 0 → prompt is cleared → "Fix and Loop" step is skipped (empty prompt) → workflow completes
- Tests failed: Exit code ≠ 0 → prompt contains error output → "Fix and Loop" executes → fixes issues → loops back to "Run Tests"
This approach avoids double-running tests in conditions and provides the AI with full test output for analysis.
Workflow structure
Tests Must Pass:
icon: ✅
menu: buttons
actions:
- name: 🧪 Run Tests
prompt:
command: 'npm test 2>&1; echo "Exit code: $?"'
- name: ✓ Clear if Passed
if:
type: shell
value: 'echo "$prompt" | grep -q "Exit code: 0"'
prompt: ''
- name: ❌ Fix and Loop
if:
type: js
value: 'prompt.trim() !== ""'
actions:
- name: 🔧 Fix Test Issues
prompt: |
The tests failed with the following output:
$prompt
Analyze the test failures and fix all issues.
instantRun: true
actions:
- 'Tests Must Pass' # Reference to self = loopUsage
Option 1: Standalone usage
Simply click the "Tests Must Pass" button in the Supercode UI:
- The workflow will run tests
- If tests fail, it will automatically fix issues
- The process repeats until all tests pass
Option 2: Use in other workflows (recommended)
Add a reference to the workflow at the end of your own workflow to guarantee quality:
Your Workflow:
icon: 🚀
menu: buttons
actions:
- name: Implement Feature
prompt: 'Implement user authentication'
instantRun: true
- name: Add Tests
prompt: 'Write tests for authentication functionality'
instantRun: true
- 'Tests Must Pass' # Guarantees test success before completionCustomization
The workflow defaults to using npm test. For other test runners, simply change the command in the first step:
# For Yarn
- name: 🧪 Run Tests
prompt:
command: 'yarn test 2>&1; echo "Exit code: $?"'
# For Python/pytest
- name: 🧪 Run Tests
prompt:
command: 'pytest 2>&1; echo "Exit code: $?"'
# For Go
- name: 🧪 Run Tests
prompt:
command: 'go test ./... 2>&1; echo "Exit code: $?"'Ralph Wiggum aka "Ralph is a Bash loop" Simple
You can download a ready-made workflow and use it in your project.
Simply extract the archive to the .supercode/workflows/ directory:
This is a port of the canonical Ralph Wiggum technique from Claude Code - an iterative AI development methodology that embodies the philosophy of persistent iteration despite failures.
Ralph Wiggum is a character from The Simpsons, known for his persistent but chaotic attempts to help. The technique embodies this spirit: deterministic iteration that may seem chaotic but ultimately gets the job done.
Ralph Wiggum Philosophy
The Ralph Wiggum technique is based on four key principles:
- Iteration > Perfection - Don't strive for perfect results on the first attempt. Let the loop refine the work.
- Errors are data - Deterministic failure means errors are predictable and informative.
- Operator skill matters - Success depends on writing good prompts, not just having a good model. LLM is a mirror of operator skills.
- Persistence wins - Keep trying until success. The loop automatically handles retry logic.
How does it work?
The classic Ralph Wiggum technique in Claude Code:
while :; do cat PROMPT.md | claude ; done
In Supercode Workflows, this is implemented through two workflows:
- Ralph Wiggum Loop (with button) - initializes iteration counter, sets system prompt, starts inner loop, cleans up counter at the end
- Ralph Iteration (inner) - increments counter, performs work, checks completion conditions, and if not complete - calls itself recursively
The loop continues until: completion signal, "stuck" signal, or maximum 20 iterations.
Critical skill: writing prompts
Success with Ralph depends on writing good prompts. Here are best practices:
❌ Bad prompt
Build a todo API and make it good.
✅ Good prompt
Build a REST API for todos. When complete: - All CRUD endpoints working - Input validation in place - Tests passing (coverage > 80%) - README with API docs Output: <promise>COMPLETE</promise>
1. Clear completion criteria
Always specify what "done" means and include a completion signal:
Implement user authentication system. Completion criteria: - JWT token generation and validation - Login/logout endpoints - Password hashing with bcrypt - Auth middleware for protected routes - Unit tests for all functions - Integration tests for endpoints Output: <promise>COMPLETE</promise>
2. Incremental goals
Break complex tasks into phases:
Build e-commerce checkout flow: Phase 1: Shopping cart - Add/remove items - Update quantities - Calculate totals - Tests for cart operations Phase 2: Checkout process - Shipping address form - Payment integration - Order confirmation - Tests for checkout flow Phase 3: Order management - Order history page - Order status tracking - Email notifications - Tests for order operations Output <promise>COMPLETE</promise> when all phases done.
3. Self-correction pattern
Guide AI to test and fix issues:
Implement feature X following TDD: 1. Write failing tests for the feature 2. Implement the feature 3. Run the tests 4. If any fail, debug and fix 5. Refactor if needed 6. Repeat steps 3-5 until all tests green 7. Verify code quality (linting, formatting) Output: <promise>COMPLETE</promise>
Usage
Basic usage:
- Write a task with clear completion criteria (see examples above)
- Include
<promise>COMPLETE</promise>in the prompt as a completion signal - Click the "Ralph Wiggum Loop" button
- Watch Ralph iterate until completion
When to use Ralph:
- ✅ Complex multi-step tasks requiring iterations
- ✅ Tasks where the first attempt may need refinement
- ✅ TDD workflows (test, implement, fix, repeat)
- ✅ Exploratory development
- ✅ Tasks with self-checking steps
- ❌ Simple single-step tasks
- ❌ Tasks requiring careful upfront planning
- ❌ Tasks requiring human decisions between steps
Safety mechanisms
Maximum iterations: Built-in limit of 20 iterations prevents infinite loops on impossible tasks.
Detecting "stuck": If AI understands it's stuck, it can output <promise>STUCK</promise> - this will stop the loop, and AI will explain what's blocking progress.
Iteration counter: Each iteration shows the current number for progress monitoring: (Iteration: 5)
Workflow structure
Ralph Wiggum Loop: # Main workflow with button
icon: 🔄
menu: buttons
actions:
- Initialize Counter # Set counter to 0
- Activate Ralph Mode # Set system prompt
- Start Iteration Loop # Call Ralph Iteration
- Cleanup # Remove counter file
Ralph Iteration: # Inner loop (no external trigger)
actions:
- Increment Counter # counter++
- Work on Task # AI works on $initialPrompt
- Loop Again # If not ready, call Ralph IterationDeep Refactoring Medium
You can download a ready-made workflow and use it in your project.
Simply extract the archive to the .supercode/workflows/ directory:
A comprehensive multi-step workflow for systematic codebase refactoring. Automatically finds duplications, plans improvements, and implements changes with validation at each step.
What does this workflow do?
Deep Refactoring performs a complete refactoring cycle in 6 stages:
- Analyze code structure - Maps all key symbols, architectural patterns, and component relationships
- Find explicit duplications - Locates copied code and repeated patterns
- Find implicit duplications - Discovers semantically similar entities that can be unified
- Create refactoring plan - Generates a step-by-step plan with risk prioritization
- Implement refactorings - Executes changes incrementally with testing after each step
- Save summary - Documents all improvements in
refactoring-summary.md
Key features
Specialized analysis modes:
SC:Architect- for structural analysis and planningSC:Refactor- for finding duplications and optimization opportunities
Incremental validation (key differentiator):
The workflow uses an internal loop that tests each refactoring separately:
- Implements one refactoring at a time
- "Tests Must Pass" runs after each change
- Next refactoring starts only if tests pass
- Easy to identify which specific refactoring caused an issue (if any)
- No regression accumulation
Concise output:
During analysis stages, the workflow produces brief bullet points (1-2 sentences per item), keeping the process focused and efficient.
Workflow structure
Deep Refactoring: # Main workflow with button
icon: 🏗️
menu: buttons
actions:
- 🔍 Analyze Code Structure # SC:Architect analysis
- 🔎 Find Explicit Duplications # Find copied code
- 🧩 Find Implicit Duplications # Find similar entities
- 📋 Create Refactoring Plan # Plan to .refactoring-plan.md
- 🔧 Execute Refactorings Loop # Start loop
- 📝 Save Summary # refactoring-summary.md
- 🧹 Cleanup # Remove temp files
Deep Refactoring Iteration: # Internal loop (no button)
actions:
- 📖 Read Current Plan # Read the plan
- 🔍 Check if More Items # Check for [ ] in plan
- 🛠️ Implement Next Item # Execute + Tests Must Pass
- Loop Recursion # Next refactoringWhen to use
Suitable for:
- ✅ Codebases with accumulated technical debt
- ✅ Projects with noticeable code duplications
- ✅ Before adding major features (clean foundation)
- ✅ After rapid prototyping phase (consolidation)
- ✅ Regular maintenance cycles
Best results when:
- You have test coverage
- Codebase is under version control
- You want systematic, not ad-hoc refactoring
Example result
Before refactoring:
src/ UserCard.tsx // 120 lines ProductCard.tsx // 115 lines (95% similar) OrderCard.tsx // 118 lines (93% similar)
After workflow:
src/
components/
Card.tsx // 80 lines (generic component)
UserCard.tsx // 35 lines (uses Card)
ProductCard.tsx // 32 lines (uses Card)
OrderCard.tsx // 34 lines (uses Card)Result: 353 lines → 181 lines, shared abstraction, easier maintenance.
Trello Task Processor Advanced
You can download a ready-made workflow and use it in your project.
Simply extract the archive to the .supercode/workflows/ directory:
A fully automated workflow for processing Trello tasks: takes a task from the Todo column, executes it with an AI agent, generates a summary, and moves it to Done.
What does this workflow do?
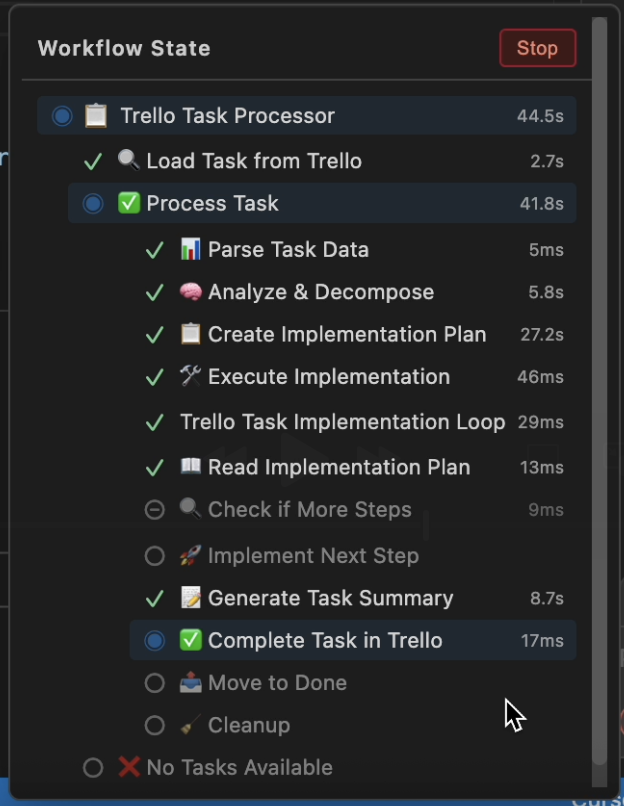
Trello Task Processor is an advanced integration workflow that automates the entire task lifecycle:
- Loads a task from the Trello Todo column (marks it as "in progress")
- Analyzes and decomposes the task using SC:Architect mode
- Creates an implementation plan with checkboxes in a file
- Executes step by step through an internal loop with testing after each step
- Generates a summary of completed work
- Moves to Done and adds the summary as a comment
Key features
Full task cycle automation:
- From task pickup to Done status - no manual intervention
- Visual indicators in Trello (card colors, prefixes)
- Automatic result documentation in comments
Intelligent processing:
- SC:Architect mode for analysis and planning
- Decomposition of complex tasks into atomic steps
- Cyclic implementation with validation
Reliability:
- Testing after each step via "Tests Must Pass"
- Error handling and edge cases
- Transparent execution status
Task lifecycle
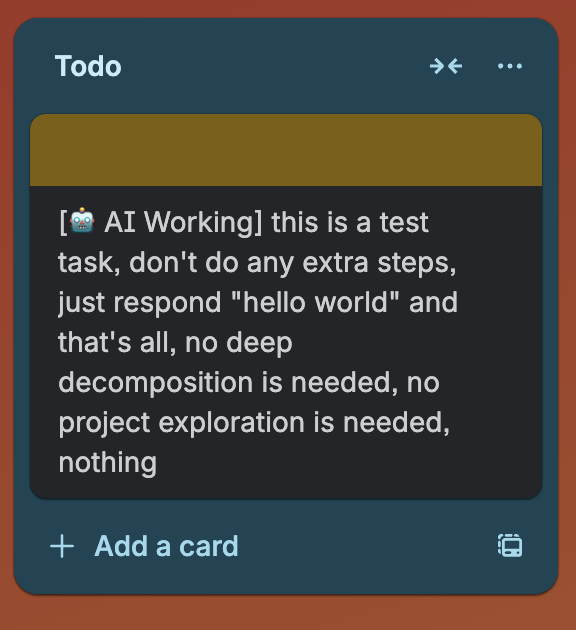
- Task in Todo - regular Trello card
- Picked up for work - prefix
[🤖 AI Working]added, card turns yellow - Analysis and planning - AI studies the task, creates a plan
- Implementation - step-by-step execution with tests
- Completed - moved to Done, card turns green, summary comment added

Workflow structure
Trello Task Processor: # Main workflow with button
icon: 📋
menu: buttons
actions:
- 🔍 Load Task from Trello # Load from Todo
- ❌ No Tasks Available # If empty - exit
- ✅ Process Task # If available:
- 📊 Parse Task Data # Parse JSON
- 🧠 Analyze & Decompose # SC:Architect analysis
- 📋 Create Plan # Plan to trello-task-plan.md
- 🛠️ Execute Implementation # Start loop
- 📝 Generate Summary # Brief summary
- ✅ Complete Task # Prepare data
- 📤 Move to Done # Move + comment
- 🧹 Cleanup # Clean up files
Trello Task Implementation Loop: # Internal loop
- 📖 Read Plan
- 🔍 Check if More Steps
if: has [ ] steps
- 🚀 Implement Next Step
- Tests Must Pass # After each!
- Loop recursion # Next stepSetup
1. Get Trello API keys:
- API Key: https://trello.com/app-key
- Token: click the "Token" link on the page above
- Board ID: open your board in browser, the URL will have
/b/BOARD_ID/...
2. Add to .env:
TRELLO_API_KEY=your_api_key_here TRELLO_API_TOKEN=your_token_here TRELLO_BOARD_ID=your_board_id_here
3. Ensure you have columns:
- Todo - for new tasks
- Done - for completed tasks
Example workflow
Task in Trello:
Title: Add user authentication Description: Implement JWT-based authentication with: - Login endpoint - Token validation middleware - Password hashing with bcrypt - Tests for auth flow
What will happen:
- Card becomes
[🤖 AI Working] Add user authentication(yellow) - AI analyzes the task and creates a plan with 6-7 steps
- Each step: implementation → tests → next step
- After completion, card moves to Done (green)
- Comment added: "✅ Task completed by AI (2026-01-15) - Implemented JWT auth with login endpoint (auth.ts), middleware (authMiddleware.ts), bcrypt hashing. All tests passing, coverage 92%."
Usage tips
- Detailed descriptions - more context in description = better results
- Atomic tasks - one task = one feature/bugfix
- Review code - do code review after execution
- Have tests - workflow relies on tests for validation
- Automation - can add
runEvery: "5m"for automatic queue processing

